The Lloyds Bank tournament was a mainstay of European chess, taking place every August for many, many years at the posh Cumberland Hotel at Marble Arch. The hotel was near Bayswater, the King’s Head Pub (where lots of people gathered to play chess, for example, Jon Speelman, Andrew Whiteley and don’t forget its “multi quiz machines”) and Raymond Keene seemed to have a hand in the organization. Keene was often spotted hobnobbing with bank executives and other OBE and MBE types. Stewart Reuben (evidently a poker player and author) was the chief TD. Amusingly, Keene co-won the tournament with Seirawan and Miles one year (1981) and I heard him say after the tournament that his proceeds would just about cover his move (to posh Kensington). Apparently his moving expenses were rather high.
News as of 2/15/08: I just learned that “Britbase” has many of the Lloyds Bank games from various years, and I learned that 1977 was the first Lloyds Bank. Jolly Argentinian personality GM Miguel Quinteros was the first winner as I see on Britbase.
We were all very young at this, the second Lloyds Bank installment. I had just popped over to the 1978 version on the ferry boat after playing in the Belgian “ECI” tournament in Eeklo. Suzzane Wood was the British Girls representative at the ECI, and Irish player Andrew McCarthy wound up winning my junior section ahead of, among others, Danish player Erik Pederson.
Here are some games I had versus well known chess personalities.
GM Heikki Westerinen (FIN) – M. Ginsburg Sicilian Scheveningen, Keres Attack
1. e4 c5 2. Nf3 d6 3. d4 Nf6 4. Nc3 cxd4 5. Nxd4 e6 6. g4 h6
In a more recent post, I discuss 6…Nc6!? here dispensing with 6….h6.
7. Bg2 Nc6 8. h3 Heikki liked this slow treatment but it should promise zero.
8…Bd7 9. O-O Nxd4 Interesting for black is 9… Be7 10. f4 Nxd4 11. Qxd4 Bc6 12. Be3 Nd7 13. Qd2 g5!? (Too ambitious? – but it pays off) 14. Bd4 Rh7 15. e5? (White misses a chance with 15. b4! to claim an edge) 15… dxe5 16. fxe5 Nxe5 17. Rad1 Qc7 18. Ne4 O-O-O 19. Qc3 Ng6 20. Bxa7 Rxd1 21. Rxd1 Nf4 22. Bf3 Nxh3+ and black won in 31 moves, Sveshnikov,E (2525)-Lputian,S (2585)/Tilburg 1992.
10. Qxd4 Bc6 More sensible is the equalizing 10… Qc7 11. Be3 Be7 12. Rad1 O-O 13. f4 Bc6 14. f5 b5 15. a3 e5 16. Qd3 a5.
11. b4 Qb6?! Here, more natural is 11… a6 12. a4 Be7 13. Be3 O-O 14. b5 e5 15. Qd3 Bd7.
12. Qc4 Be7 13. Be3 Qd8 14. Rad1 14. b5 Bd7 15. e5 Rc8 is OK for black.
14… Rc8 15. Qb3 Qc7 16. Rd3 b6 Again, more natural is 16… a6 17. a4 O-O 18. b5 Be8.
17. f4 g6 Black can defend after 17… O-O 18. g5 hxg5 19. fxg5 Nh5 20. g6 Bd7 21. Rxf7 Rxf7 22. gxf7+ Kxf7 23. Bf3 g6 with chances.
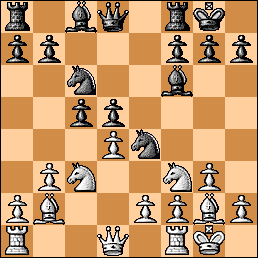
18. Rf2 Nd7 19. Bd4?! (Indicated is 19. a4!) 19… O-O 20. f5 Bh4 21. Rfd2 Bg5 22. Rd1 Possible is 22. fxe6 Bxd2 23. Rxd2 Ne5 24. b5 Bb7 25. Nd5 Bxd5 26. exd5 Qe7 27. Re2 fxe6 28. dxe6 Kh7 and the game is level. The game toddles on with both sides continuing to commit inaccuracies.
Position after 22. Rd1 – chances are about level.
22… Rfe8 The primitive and somewhat surprising 22… exf5!? 23. gxf5 gxf5 24. Nd5 Bxd5 25. Qxd5 Ne5 26. Rc3 Qb8 27. exf5 Rxc3 28. Bxc3 Rc8 is about even.
23. Bf2 Ne5? Again, the computer-like 23… gxf5 is fine. 24. gxf5 Ne5 25. Rxd6 exf5 and black has no problems at all.
24. Rxd6 Ba8 25. Nb5 Qxc2 26. Nxa7 Qxb3 27. axb3 Rc2 28. fxe6 fxe6 29. Bd4? This is a bad blunder. The simple 29. Rxb6 gives white a significant edge.
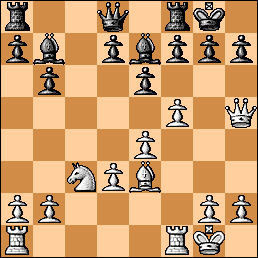
Position after the 29. Bd4? miscue.
29…Rxg2+! Of course. Black gets an initiative.
30 .Kxg2 Bxe4+ 31. Kf1?! If 31. Kg3!, 31…Nd3! 32. Rxd3 Bxd3 33. Nc6 Be4 leads to a small white edge. The text should have tossed any winning chances down the drain.
31…Rf8+ 32. Bf2 If 32. Ke1 Nd3+ and draws.
32… Be3?? What’s this? A bad tactical blackout. The obvious 32… Bh4 33. R1d2 Nd3 draws with no problem, for example 34. R6xd3 Bxd3+ 35. Kg1 Bxf2+ 36. Rxf2 g5 37. Nc6 Be4 38. b5 Bd3 39. Ne7+ Kg7 40. Rxf8 Kxf8 41. Nc8 Bxb5.
33. Rd8! Oops. Now white just wins. Boo!
33…Bg5 34. Rxf8+ Kxf8 35. Bxb6 Bc2 36. Re1 Nd3 37. Rxe6 Bxb3 38. Re4 Bd2 39. Ke2 Bd5 40. Kxd3
Black resigns. Really a poor game.
1-0
M. Ginsburg – Julian Hodgson (2255) Tarrasch Defense
This is one of those pre-database encounters. I cannot find it in the regular online sources.
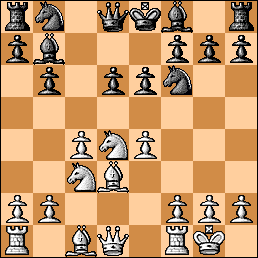
1. c4 e6 2. Nf3 d5 3. b3 c5 4. g3 Nc6 5. Bg2 Nf6 6. O-O Be7 7. Nc3 O-O 8. cxd5 exd5 9. d4 Ne4 10. Bb2 Bf6
Position after 10…Bf6. So far, so normal.
11. e3?! Much stronger is 11. Na4! hoping for 11…b5? (11… b6 is correct) 12. Nxc5! Nxc5 13. Rc1! with a white edge. Many games have seen black fall into this trap, for example Stefansson,H (2470)-Bosch,J (2305)/Arnhem 1989, 1-0, 34. The variation 11. Na4 b6 occurred in a hugely entertaining and wild game between Bent Larsen and Margeir Petursson. Let’s see it:
11. Na4 b6 12. Rc1 Ba6 13. dxc5 Bxb2 14. Nxb2 bxc5 15. Nd3 Re8 16. Re1 Qb6 17. e3 Rad8 18. Bf1 c4 19. Nf4 Nb4 20. Ra1 Qf6 21. Kg2 Nc3 22. Qc1 Ncxa2 Craziness on the board!
23. Qa3 cxb3 24. Qxb3 Bc4 25. Bxc4 dxc4 26. Qxc4 Rc8 27. Qb3 Qc3 28. Qa4 Qc4 29. Reb1 a5 30. Qxa5 Ra8 31. Qh5?? Here, the amazing shot is 31. Qf5!! and white is better. There follows 31…Nc2 (31… g6 32. Qg5 Nc2 33. Nd5 Re6 34. Nf6+ Kg7 35. Ng4 Kg8 36. Qh4 Qa6 37. Nh6+ Kg7 38. Nxf7 is overwhelming for white) 32. Nd5 Nxa1 33. Ng5 and white has successfully won the day.
31… Nc2 32. Rb6 Nxa1 This is just a bluff on white’s part. 33. Ng5 h6 34. Rxh6 gxh6 35. Qxh6 Ra6? (35… Nc2 wins; white has no discernible threat.) 36. Qh7+ Kf8 37. e4 Here Bent could have launched with 37. Nfe6+!? Raxe6? (37… Qxe6 38.Nxe6+ Rexe6 39. Qh8+ Ke7 40. Qxa1 Nb4 41. Qb1 Rab6 42. h4 Nd5 43. Qf5 Rb5 with complete insanity) 38. Qxf7 mate – the rather rude point.
37… Rf6 38. Nd5 Rxf2+ 39. Kxf2 Qd4+ 40. Kf3 Qg7 41. Qf5?? The right move is 41. Qh4! with an edge. If 41…Qg6 (41… f6 42. Nh7+ Kf7 43. Nhxf6 Rh8 44. Qf4 Qf8 45. Qf5 Qa3+ 46. Kg4 Qd6 47. Nh5+ Ke8 48. Qc8+ Qd8 49. Qe6+ Kf8 50. Qf5+ Kg8 51. Qg6+ Kf8 52. Qg7+ Ke8 53. Ndf6+ Qxf6 54. Nxf6+ Kd8 55. Qd7 mate!) 42. Qh8+ Qg8 43. Nh7 mate)
41… Qg6 Now black is winning. The crazy game with all its roller-coaster fortune changes is almost over. Poor Bent. 42. Qf4 (42. Nh7+ Kg7) 42… Nc2 43. Nf6 Rd8 44. Qe5 Nd4+ 45. Kg2 Nc6 46. Qb2 Nab4 47. h4 Ke7 0-1 Larsen,B (2520)-Petursson,M (2535)/Gausdal 1985.
Back to the Hodgson game.
11… Bg4 Young Julian has no problems at all.
12. h3?! Another bizarre choice. However, 12. Ne2 Qa5 13. Re1 Rfd8 14. h3 Bxf3 15. Bxf3 Ng5 16. Bg2 Ne6 17. Qc1 cxd4 18. Nxd4 Re8 19. Qd1 Nexd4 20. Bxd4 Bxd4 21. exd4 Re4 22. Rxe4 Qb6 and white resigned, (Young) Georgiev,V (2245)-Dobrev,N (2310)/Shumen 1995 was not a good white experience either.
12… Bxf3 13. Bxf3 cxd4 14. Nxe4 dxe4 15. Bxe4 dxe3 16. Qxd8 exf2+ 17. Rxf2 Bxd8
To sum up the opening, white has played like an idiot, lost a pawn, and faces an uphill struggle to draw. Not good “preparation.” I achieve the draw by making some tricks with the bishop pair in order to get bishops of opposite colors. Even that finale contained some dangers, but in the end I figured out a drawing formation.
18. Kg2 Bb6 19. Rd2 Rad8 20. Rad1 Rxd2+ 21. Rxd2 Rd8 22. Rxd8+ Bxd8 23. a3 g6 24. Kf3 Kf8 25. b4 a6 26. a4 Nxb4 27. Ba3 a5 28. Bxb7 f5 29. g4 fxg4+ 30. Kxg4 Kf7 31. Bxb4 axb4 32. Kf4 Kf6 33. Bd5 h5 34. Bb3 Bc7+ 35. Ke4 Kg5 36. Kf3 Kh4 37. Kg2 g5 38. Bc4 g4 39. hxg4 hxg4 40. Be6 Kg5 41. Kf2 Kf4 42. Kg2 Bb6 43. Bb3 Kf5 44. Kg3 Bc7+ 45. Kg2 Ke4 46. Be6 Kf4 47. Bb3 Kf5 48. Bd1 Kg5 49. Bb3 Kh4 50. Be6 g3 51. Kf3 b3 52. Kg2 b2 53. Bf5 Bb6 54. Bb1 Kg4 55. Bh7 Kf4 56. Bb1 Ba5 57. Bh7 Be1 58. Bb1 Ke5 59. a5 Kd6 60. a6 Kc7 61. Bd3 Kb6 62. Kf3 Bf2 63. Kg2 Kc7 64. Kf3
1/2-1/2
At least I held a draw after the gruesome debut.
Andrew Martin (2340) – M. Ginsburg Sicilian Irregular, early ….b6
1. e4 c5 2. Nc3 b6 3. Nf3 Bb7 4. d4 cxd4 5. Nxd4 Nc6 6. Be3 e6 7. Bd3 Nge7!? An interesting position that hasn’t been seen much. Also possible is 7… Nf6 8. f4 Bb4 9. Qf3 Rc8?! (Here, 9… d5! 10. e5 Ne4 11. Nde2 Nc5 12. O-O-O Nxd3+ 13. Rxd3 O-O looks OK for black) 10. O-O Bxc3 11. bxc3 d5 12. e5 Nxd4 13. cxd4 Ne4 14. f5 exf5 15. Qxf5 led to rapid white victory in 25 moves, Braghetta,S-Perovic,B/Toscolano 1996.
8. O-O The positional and sophisticated treatment, not one for a legendary hacker like Andrew, is 8. Ndb5! Ng6 9. Be2 d6 10. O-O Be7 11. a4 O-O 12. Qd2 a6 13. Na3 with a nagging edge.
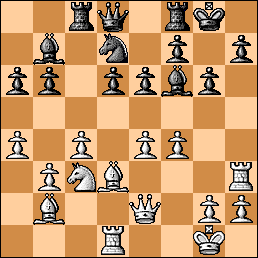
8… Nxd4 9. Bxd4 Nc6 10. Be3 Be7 11. Qh5 Nb4 12. f4 Nxd3 13. cxd3 O-O 14. f5
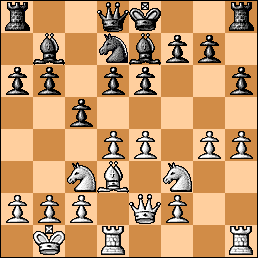
Position after 14. f5
14…d5 It is more sensible to defend with 14… Bf6 15. Rf3 g6 16. fxg6 fxg6 and black is all right. The text looks nuts but it can be justified with a rather difficult variation on the next move (15…exf5!).
15. Rf3 h6? The most tactically alert reaction is 15…exf5! 16. Rh3 h6 17. Bxh6 g6! 18. Rg3 Qd6! threatening Qxg3 with an unclear game after 19. Bxf8 Bxf8. Weaker is 15… dxe4 16. Rh3 h6 17. Bxh6 gxh6 18. Qxh6 Qd4+ 19. Kh1 Qg7 and this is losing for black after 20. Rg3.
16. Rg3 dxe4 17. dxe4 This is bad for black, but not lost yet.
17…Bc5?? This should lose immediately. 17… Bf6 18. Qxh6 exf5 19. Qh5 Be5 holds on, with white retaining an edge.
18. Qxh6? The flaw in black’s thinking is exposed by the brutal 18. Rxg7+!! Kxg7 19. Qxh6+ Kg8 20. Bxc5 bxc5 21. f6 Qd4+ 22. Kh1 and after that spite check, black has to resign.
18… Bxe3+ 19. Qxe3 exf5 20. Rd1? Here white misses another great blow: 20. Nd5!! – the point of this zinger is to block black’s response Qd4+ when white plays Qe3-h6.
Position after 20. Nd5!! (Analysis) – A fantastic shot.
There is no defense. For example, 20…Bxd5 (20… f6 21. Nf4 Qe7 22. exf5 Qxe3+ 23. Rxe3 wins) and now the delightful 21. Qh6! g6 22. Rh3! and mates! The desperate 20…Kh8 is crushed by the nice maneuver 21. Qc3! f6 (forced) 22. Nf4! and wins.
20… Qf6 21. Rf1 Rad8 22. Rxf5 Qd4 23. Nd5 Qxe3+ 24. Rxe3 f6 1/2-1/2
Of course, white still has an edge in this ending, but it’s nothing like before. It’s quite possible he had spotted some of the decisive variations listed above after he made his move, a common phenomenon with human players and very disheartening. Disgusted, he “throws in the towel” with a draw offer and we head off to the pub.
NM Colin Crouch (2300) – M. Ginsburg Sicilian 2. c3 Lloyds Bank, Round 10
1. e4 c5 2. c3 The move 2. c3 brings a general air of irritation to the proceedings.
2…g6 3. d4 cxd4 4. cxd4 d5 5. exd5 The move 5. e5 is a whole different story. These days, 5. e5 is considered the most promising way to try to achieve a small edge. The text should achieve very little.
5…Nf6 6. Nc3 Nxd5 It’s more usual to play 6… Bg7 7. Bc4 O-O 8. Nge2 Nbd7 9. Nf4 (not 9. O-O Nb6 10. Bb3 Nfxd5) 9… Nb6 10. Bb3. In the 70s and 80s this was explored quite a bit. However, black should be OK. For example, 10… a5 11. a4 (unpromising is 11. a3 a4 12. Ba2 Bf5 13. O-O Qd7 14. Qe2 h6 15. h4 Rac8 16. Be3 Ne4 and black is active) 11… Qd6 (Nimzovich wouldn’t like using the queen as a ‘blockader’ but this move has its points, the queen eyes the important squares b4 and f4) 12. O-O Bd7 13. Qe2 and now a sample continuation is 13…Rfe8 (Is this natural move a TN? – prior games from British player Wade have seen the unnatural 13…Rfc8) 14. Re1 Rac8 15. h3 h6!? (We’ll see the point of this mysterious move shortly) 16. Nb5 (What else?) 16…Qb4 17. Ra3 Bxb5 18. axb5 a4 19. Ba2 g5! 20. Nd3 Qxb5 and black is fine.
7. Bc4 Nb6 8. Bb3 Bg7 9. Nf3 O-O 10. O-O Bg4 11. d5 N8d7 12. h3 Bxf3 13. Qxf3 Rc8 14. d6 TN A novelty from Mr. Crouch! Colin was very nervous at the board and reminded me of USA’s own Walter Browne. Previously seen was the poorly played game 14. Re1 Nc5? (Correct is 14…Ne5! 15. Qe2 Re8 16. Bg5 Qd7 and it’s equal; same goes for 16. Bf4 Nec4) 15. Bg5 Nxb3? 16. axb3 Bxc3 17. bxc3 Qxd5 18. Qxd5 Nxd5 19. c4 and white won shortly, Abbasov,F (2290)-Hussan,M (2108)/Abu Dhabi 1999. This massacre is a good cautionary tale against opening up the a-file when it’s not warranted. Objectively Crouch’s TN in my game promises nothing.
14… exd6 15. Qxb7 Nc5 16. Qf3 Qf6?! The most accurate was 16… d5! 17. Rd1 Ne6! but this requires tactical alertness. The point is 18. Nxd5 (18. Qg4 h5 19. Qb4 d4 is unclear) 18… Nd4! 19. Rxd4 Bxd4 20. Qe4 Bc5 21. Bh6 Nxd5 22. Bxd5 Qf6 23. Bxf8 Qxf2+ and black is very happy. More to the point, this line does not liquidate into a boring ending as the text does and keeps winning chances.
17. Qxf6 Bxf6 18. Nb5 d5 Playable and probably better is 18… Rfd8 19. Bf4 Rd7 20. Nxd6 Rcd8 21. Bxf7+ Rxf7 22. Nxf7 Kxf7 23. Rfd1 Nd3 24. Bc7 Rd4 25. Bxb6 axb6 26. Rd2 Bg5 and white is a very tiny bit better, maybe. Black should be able to draw it.
19. Be3 Bxb2 20. Rab1 Be5 21. Nxa7 Rc7 22. Nb5 Rcc8
Agreed drawn. White has a small edge and can and should play on, for example 23. Rbd1 Rfd8 24. Rfe1 Bf6 25. Re2 Nxb3 26. axb3 Rb8 27. Red2 Rb7 28. g4 and white can certainly try here. Maybe Colin’s nerves were frazzled from the perplexities of his innovation.
1/2-1/2
Kevin J. Wicker (2305) – M. Ginsburg Trompovsky (“Ruth’s”), Round 8 Lloyds Bank 1978
My opponent was British Boys U-18 co-champ in 1970!
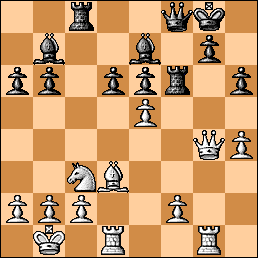
1. d4 Nf6 2. Bg5 e6 3. e4 h6 4. Bxf6 Qxf6 5. Nf3 b6 6. Bd3 Bb7 7. Qe2 d6 8. Nc3 Qd8 9. O-O-O Be7 10. Kb1 a6 11. g4 Nd7 12. h4 c5 Playable is 12…b5!? The text looks suspicious but maybe it’s all right.
Position after 12…c5. Perplexing.
13. g5 cxd4?! With hindsight, 13…b5! is much better. Then, 14. dxc5 Nxc5 offers balanced chances since 15. e5 d5! promises nothing.
14. Nxd4 Ne5 15. g6!? A weird idea that leads to equality. White had the simple 15. f4 Nxd3 16. Qxd3 with an advantage.
15…Nxg6 16. Nxe6 fxe6 17. Qh5 O-O 18. Qxg6 Rf6 19. Qg4 Qf8 20. Rhg1 Rc8 20…Qf7 21. Bc4 b5 22. Bb3 Re8 23. Rd3 Bf8 24. f3 b4 25. Ne2 d5 26. h5 a5 is about even. Nothing is really going on.
21. e5?! Impetuous and not very good.
Position after 21. e5?! – one mistake leads to another.
21… dxe5? And a mistake in reply. Of course throwing in 21… Bf3! is correct; the lame 22. Qxg7+? Qxg7 23. Rxg7+ Kxg7 24. Rg1+ Kf7 leaves black better. The queen sacrifice is white’s best try but black can defend: 21…Bf3 22. exf6! Bxg4 23. fxe7 Qf4! 24.Rde1 Bf5 and black is better. White has 25. Nd5!? but black can defend simply enough with 25…exd5 26. Bxf5 Qxf5 27. e8=Q+ Rxe8 28. Rxe8+ Kf7! 29. Rb8 Qxf2 and whatever advantage there is rests with black in this ending. It is most likely drawn.
22. Ne4 Rf4 23. Qxe6+ Kh8 24. Qg6 Qf7 25. Nd6 Qxg6 26. Bxg6 Bxd6 27. Rxd6 Rxh4? Black had the simple 27… b5 28. Rb6 Bc6 29. Rxa6 Rxf2 30. Ra7 Rcf8 31. Rc1 e4 and he’s all right.
28. Rxb6 Rc6 Black uses the trick 29. Rxb7? Rxg6! with bank rank mate after 30. Rxg6? Rh1+. However, white simplifies and black still has some problems to solve.
29. Rxc6 Bxc6 30. Kc1 Kg8 31. Re1 Rh1 Now it’s no fun to play 31… e4 32. Rd1 Kf8 33. Rd6 Bb5 34. Re6 Rh1+ 35. Kd2 Rf1 36. Ke3 Re1+ 37. Kd4 Re2 38. c4 Bd7 39. Rxa6 Rxb2 40. Bxe4 Rxf2 41. c5 and white has a huge edge. Black plays the relatively best move. Still, this ending has some nasty pitfalls.
32. Rxh1 Bxh1 33. Kd2?! White isn’t playing so well either. He had 33. c4! to keep the black bishop off the d5-g8 diagonal.
33… Kf8 34. Ke3 Again, 34. c4! Ke7 35. Ke3 Kf6 36. Be8 with torture.
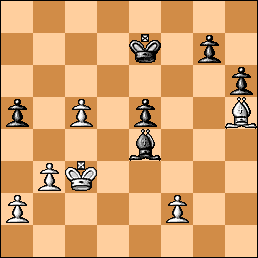
34… Bd5 35. b3 Ke7 36. c4 Bb7?? A dreadful blunder. After the obvious 36…Be6 37. c5 a5 no win for white can be seen. Furthermore, if white gets too frisky he can even lose! Here is a nice variation: 38. Kd3 Bd5! 39. Kc3 Kf6 40. Be8 Ke7 41. Bh5 Be4! (An excellent and counter-intuitive move, blocking a pawn, to enforce g6 to get the remote passed pawn rolling)
Position after 41…Be4! (analysis) – get the doggies rollin’
Continuing, 42. a3 g6 43. Be2 h5 44. b4 axb4+ 45. axb4 h4 46. Bf1 (or 46. Bg4 Bg2 and wins) 46…g5 47. b5 g4 and black wins! This is a good example of what happens when one side ignores the potential of the other side. Another strange and tactical variation is 36…Be6 37. Kd3 Bg4! 38. b4 h5 39. Ke4 Kf6 40. f3! Be6! 41. Bxh5 Bxc4 42. a3 Ke6 and it’s drawn.
37. b4 Kf6 38. Be8 Ke7 39. Bh5 Kf6 40. a4 Now the pawns roll and it’s all over. Terrible ending play by black.
40…g6 41. Be2 Ke6 42. c5 h5 43. b5 axb5 44. axb5 Bd5 45. b6 h4 46. Bg4+ Ke7 47. f4 Kf6 48. Bc8 exf4+ 49. Kxf4 g5+ 50. Kg4 Ke5 51. b7 1-0
Boo.
It’s really too bad Lloyds Bank stopped sponsoring this fantastic August event. Can we hope for its return? It was last held, I believe in 1994, featuring a very young Alexander Morozevich capturing the honors. Indeed, as a ChessBase report on Melody Amber states, “Morozevich is a brand-name for mind-boggling chess, ever since he made his international break-through at Lloyds Bank in 1994, where at the age of seventeen he took first prize with a staggering 10.5 out of 11 score, using unusual and outdated openings. “
Britbase!
All hail Britbase. Here’s a frothy encounter I dug up from the 1981 Lloyds Bank, courtesy of Britbase PGN.
Entertainingly, my opponent during the game assembled 4 espressos all in a row. Maybe one too many? In the game, a perhaps unique thing occurred in the opening – check the note to my 12th move.
M. Ginsburg – Yves Duhayon (BEL) Lloyds Bank 1981, 8/25/81 Round 6 Sicilian/Hedgehog Irregular
1. c4 e6 2. Nf3 c5 3. Nc3 b6 4. e4 Bb7 5. d4 cxd4 6. Nxd4 Bb4 7. Ndb5! Nf6 8. Nd6+ This is the first Nd6+ move. See note to my 12th move. 8… Bxd6 9. Qxd6 Bxe4 10. Nb5 Na6 11. Qa3! Very energetic. White has massive compensation.
11… Nc5 12. Nd6+ Is this a world record? This is the second time a knight has arrived on d6 with check in the opening. Readers, do you know of a clever way to go through databases to search for this?
12…Ke7 13. Nxe4 Nfxe4 14. b4 Nb7 15. Qf3 d5 16. Bd3 Qd6 17. O-O Qxb4 Condemned man // hearty meal.
18. cxd5 exd5 19. Bxe4 dxe4 20. Qg3 Everything happens with gain of time, a sure sign the initiative will prevail. Black is being knocked around like a punching bag.
20…Qd6 21. Qxg7 Rag8 22. Bg5+ Ke8 23. Qf6 h6 24. Rfd1 Qxf6 25. Bxf6 Rh7 26. Rac1
A particularly gruesome mating attack is on the board. Black is forced to give up.
1-0
Readers’ Help Needed
Readers: does anyone have a summary list of the LB winners from 1977 to 1994?
Photo Time
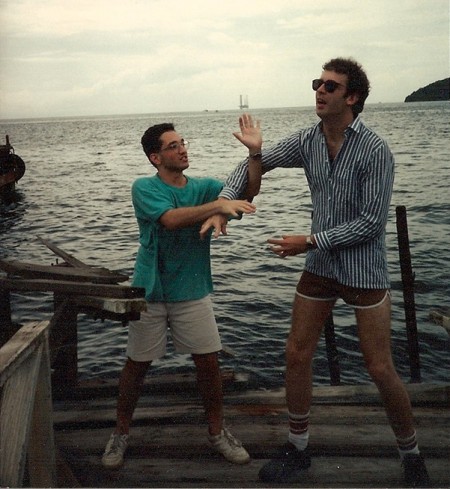
Let’s wrap up with a photo from the 1991 Lloyds Bank.
From left: British Women’s many-time champion Sheila Jackson, the author, Sarah Christopher (now de Lisle), and Fenella Cohen. Lloyds Bank 1991, Cumberland Hotel, Marble Arch, London, England